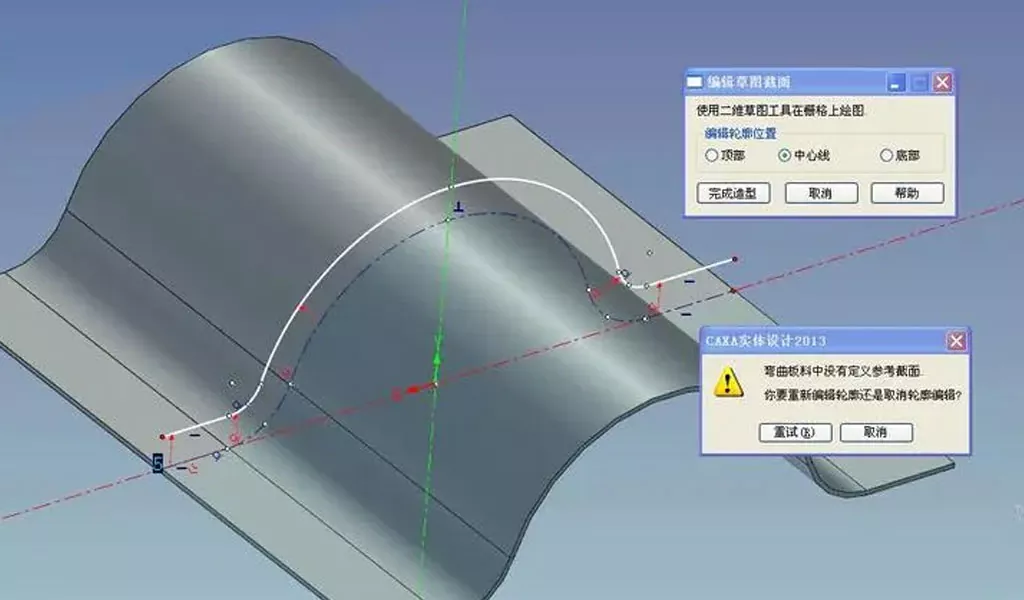
Bending sheet metal parts is a common fabrication process used to create various components and structures. It involves deforming a sheet metal workpiece to achieve desired angles or shapes.
Material Type
Different materials have different properties when bent. Consider factors such as ductility, hardness, and springback characteristics.
Material Thickness
Thicker materials require more force to bend and may require specialized equipment or techniques.
Material Grain Direction
Sheet metal often has a grain direction, which can affect its bendability. Bending across the grain can result in better outcomes.
Material Properties
Understand the specific properties of the material, such as yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, and hardness, which can affect the bending process.
Bend Radius
The radius of the bend determines how tightly the material will be bent. Smaller bend radii require more force and can lead to increased springback.
Bend Angle
The desired angle of the bend influences the setup, tooling, and machinery required for the bending process.
Springback
Most materials have a tendency to spring back slightly after being bent. Understand the springback characteristics of the specific material and adjust the bending process accordingly.
Tooling Selection
Choose the appropriate bending tools, such as dies and punches, based on the material, thickness, bend radius, and desired bend angle.
Die Width
The width of the die affects the accuracy and consistency of the bend. Wider dies provide better support and minimize distortion.
Punch Radius
The radius of the punch determines the smoothness of the bend. Smoother punches result in cleaner and more precise bends.
Lubrication
Apply lubricants or anti-friction coatings to reduce friction between the sheet metal and the bending tools. This helps prevent scratching, galling, or surface damage.
Machine Tonnage
Ensure that the bending machine has sufficient tonnage capacity to handle the material thickness and required bending force.
Machine Speed
The speed at which the bending operation is performed can affect the quality and accuracy of the bends. Optimize the speed based on the material and machine capabilities.
Machine Accuracy
The precision and repeatability of the bending machine are crucial for achieving consistent and accurate bends. Regular maintenance and calibration are essential.
Machine Tooling Setup
Proper alignment, adjustment, and setup of the bending machine’s tooling are necessary to achieve the desired bend angles and dimensional accuracy.
Part Orientation
Determine the optimal orientation of the part on the bending machine to achieve the desired bend direction and minimize distortion.
Part Positioning
Ensure proper positioning and alignment of the part within the bending machine to prevent misalignment or off-center bending.
Part Geometry
The complexity of the part’s shape and geometry affects the bending process. Consider factors such as multiple bends, curves, or intricate features.
Part Size and Dimensions
The size and dimensions of the part influence the choice of equipment, tooling, and handling methods during the bending process.
Tolerances
Understand the required dimensional tolerances for the part and adjust the bending process accordingly to meet those specifications.
Flange Length
Determine the minimum required flange length based on the material thickness and bend radius to prevent cracking or failure at the bend line.
Bend Allowance
Calculate the appropriate bend allowance to compensate for material thickness and springback, ensuring accurate final dimensions.
Bend Order
Plan the sequence of bends to minimize interference, distortion, or damage to previously bent areas.
Sheet Metal Orientation
The orientation of the sheet metal in relation to the bending direction can impact the bending process. Consider how the sheet metal should be positioned for optimal results.
Operator Skill and Training
Proper training and experience for the operator are crucial to ensure accurate and consistent bending. Skilled operators can adjust parameters and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Safety Precautions
Follow safety guidelines and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when operating bending machinery to prevent accidents or injuries.
Edge Quality
Consider the condition of the edges, such as burrs or sharp edges, and address them appropriately to avoid interference during bending or potential damage to the material.
Welding or Joining Requirements
Take into account any subsequent welding or joining processes that may be required after bending and ensure adequate access and preparation for those operations.
Surface Protection
Determine if the sheet metal surface requires protection or masking during the bending process to prevent scratches or damage.
Post-Bend Processing
Consider any additional post-bend processes, such as deburring, surface finishing, or painting, and plan accordingly to maintain the integrity of the bent parts.
Tooling Condition
Ensure that the bending tools, including dies, punches, and v-dies, are in good condition and free from damage or wear that could affect the bending process.
Lubricant Compatibility
Choose a lubricant that is compatible with the specific material being bent to ensure optimal performance and prevent any adverse reactions.
Workholding and Clamping
Securely hold the sheet metal in place during bending to prevent slippage or movement that can lead to inaccurate bends.
Workpiece Support
Provide adequate support to the sheet metal throughout the bending process to minimize distortion or sagging.
Temperature Effects
Consider the temperature of the material and the environment, as temperature variations can affect the material’s behavior during bending.
Material Handling
Ensure proper handling techniques to prevent damage or distortion of the sheet metal before and during the bending process.
Bending Machine Controls
Familiarize yourself with the controls and settings of the bending machine to adjust parameters such as speed, tonnage, and stroke length for optimal bending.
Operator Communication
Maintain clear communication between the operator and other team members to ensure smooth coordination during the bending process.
Part Design Considerations
Optimize the design of the part for bending, taking into account factors such as symmetry, avoidance of sharp corners, and appropriate bend radii.
Prototype Testing
Conduct testing on prototypes or sample pieces before mass production to verify the feasibility of the bending process and make necessary adjustments.
Tooling Maintenance
Regularly inspect and maintain bending tooling to ensure optimal performance, accuracy, and longevity.
Scrap and Material Loss
Consider the amount of material lost during the bending process due to trimming, scrap, or waste, and account for it in material calculations.
Economic Feasibility
Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the bending process, considering factors such as material utilization, setup time, and production volume.
Production Efficiency
Optimize the bending process for efficiency, considering factors such as batch sizes, setup time reduction, and production flow.
Environmental Impact
Consider the environmental impact of the bending process, such as energy consumption, waste management, and the use of environmentally friendly lubricants.
Documentation and Quality Control
Maintain proper documentation of the bending process parameters, inspection records, and quality control measures to ensure consistent results.
Compliance with Standards
Adhere to applicable industry standards and regulations regarding sheet metal bending, ensuring product quality and safety.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly assess the bending process, collect feedback, and implement improvements to enhance productivity, quality, and efficiency.
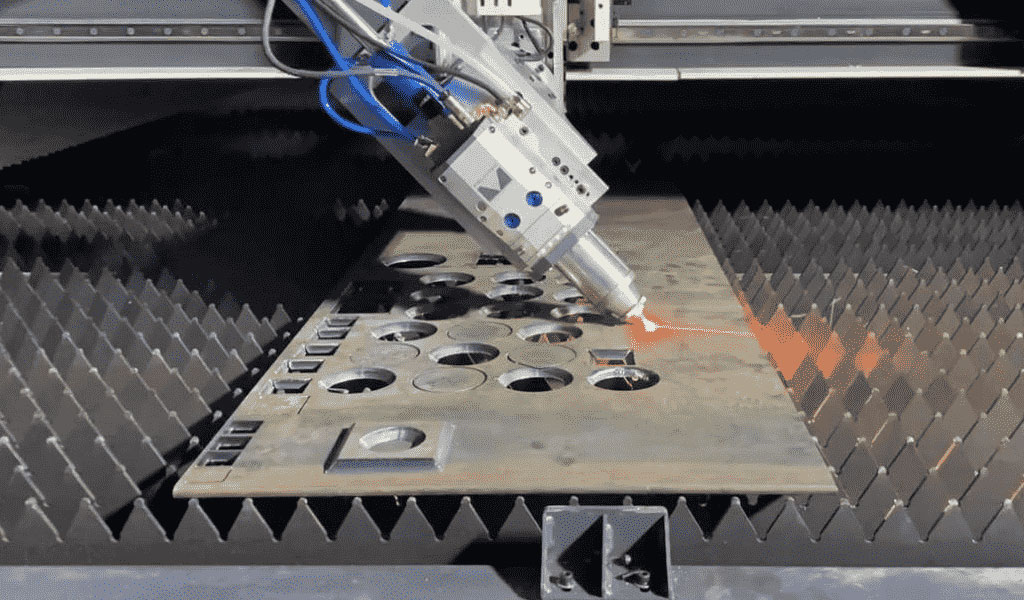
China Sheet Metal Fabrication Manufacturer
Custom precision metal fabrication services. Product specialties include UL® certified NEMA enclosures for various environmental conditions. Capabilities include punching, shearing, laser cutting, bending, machining, press brake forming, and welding. Materials worked with include mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Production volumes range from prototype to 10,000 pieces annually. Contract options include discrete orders, blanket orders, quarterly buys, and annual contracts. Value added services include inventory management, rapid prototyping, process development, design for manufacturability, inspection, supply chain management, transportation, and logistics. Industries served include aerospace, automotive, defense, electronic, electrical, entertainment, food and beverage, health, industrial automation, machinery, medical, oil, energy, power, sporting goods, telecommunications, transportation, and more.
using high quality materials
for your sheet metal parts orders
We uses a wide range of material selections for our sheet metal fabrication process. Among our materials are aluminum, stainless steel, brass, magnesium, copper, carbon steel, bronze, galvanized steel, and more. Each material is available in different grades and varieties. Rest assured that all the materials used for your sheet metal parts are durable, corrosion-resistant, long-lasting, rust-proof, wear-resistant, and high-performance. If you want a specific material to be used in the sheet metal fabrication process, don’t hesitate to contact us!
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Magnesium
- Bronze
- Galvanized Steel
Why BE-CU is Trusted by 1000+ Clients
Our sheet metal fabrication covers a lot of benefits to many industries, businesses, or projects. Below are the advantages of our services.
- Affordable and Fast Production:We can quickly produce different sheet metal prototypes and final products. KDM offers speedy production while assuring high precision. Our high-volume production also allows us to have cost-effect sheet metal fabrication services.
- Excellent Strength to Weight Ratio:Through our advanced sheet metal fabrication, we can produce sheet metal parts that are lightweight yet durable. We assure high strength, scratch resistance, and corrosion resistance to all produced sheet metal products.
- Wide Range of Materials and Techniques Used:We are experts in different sheet metal fabrication techniques that allow us to produce complex parts with additional intricate features such as notches, slots, holes, etc. Our wide range of sheet metal materials can also withstand electrical, high heat, corrosion, and more.
Online Contact China Precision Sheet Metal Manufacturers
As a direct supplier of precision machined and finished complete components to all segments of the aerospace, semiconductor, automotive, and medical industries, including innovative high tech startups, BE-CU Sheet metal manufacturer is your trusted source for precision sheet metal fabrication services.
To learn more about our aluminum,stainless steel and other steel alloy sheet metal fabrication services, contact us, or give us a call at +86 153 8731 8440, and one of our expert associates will assist you. BE-CU is your trusted source for premium sheet metal fabrication services and metal spinning china manufacturer.