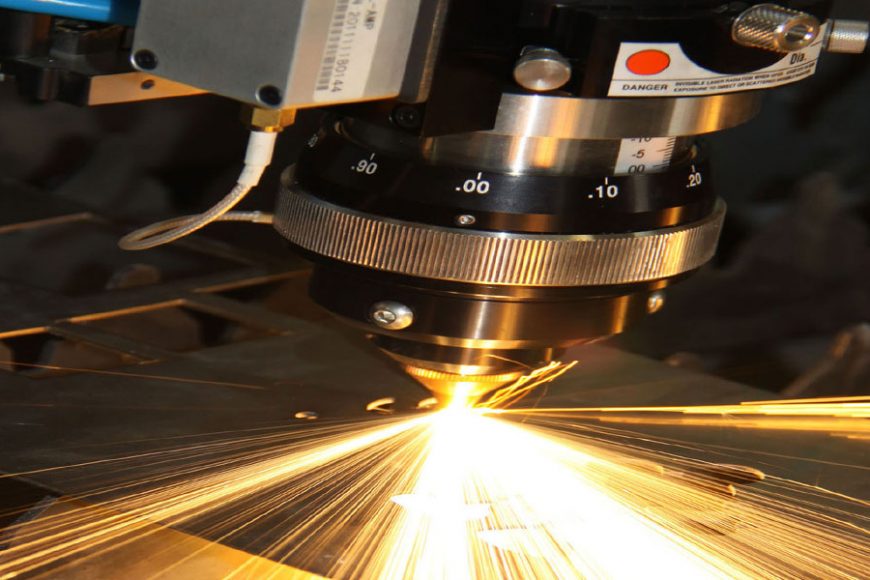
Micro laser cutting is an advanced manufacturing process that utilizes highly focused laser beams to cut intricate patterns and shapes with extreme precision and accuracy. This technology has gained widespread recognition across various industries due to its ability to create intricate designs on a miniature scale, catering to the demands of modern technological advancements. From medical devices to electronics, micro laser cutting has revolutionized the way intricate components are fabricated, enabling the production of smaller, more complex parts with unparalleled precision.
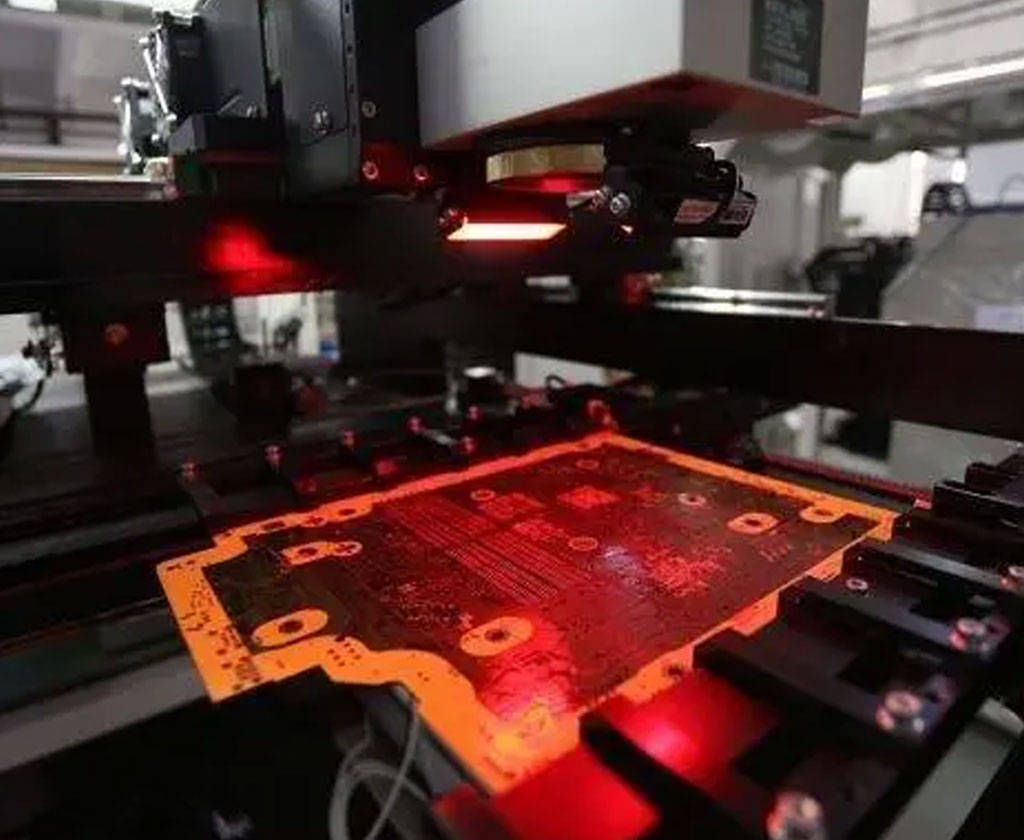

Image From https://be-cu.com/micro-laser-cutting/
What Is Micro Laser Cutting Technology
Micro laser cutting technology is a highly advanced and precise method of cutting materials, typically on a micro-scale, using focused laser beams. This innovative technology is employed across various industries to create intricate patterns, shapes, and components with unparalleled precision and accuracy.
Principles of Micro Laser Cutting
Micro laser cutting involves the use of a high-energy laser beam that is focused onto the surface of a material, effectively melting, burning, or vaporizing it along a predetermined path. The laser beam is directed through a series of mirrors and lenses to ensure its concentration onto the material, often with pinpoint accuracy.
Components of Micro Laser Cutting Systems
Laser Source
The heart of micro laser cutting systems is the laser source, which emits the high-powered beam used for cutting. Different types of lasers, such as fiber, CO2, or solid-state lasers, are utilized based on the material being cut and the required precision.
Optics and Beam Delivery System
Optical components, including mirrors and lenses, are employed to guide and focus the laser beam onto the material. The beam delivery system ensures the precise positioning and alignment of the laser for accurate cutting.
CNC Controller
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems control the movement and operation of the laser cutting machine. These systems are programmed with design specifications to direct the laser beam along the desired cutting path with exacting precision.
Workpiece Holding and Positioning Systems
For precise and accurate cutting, the workpiece needs to be securely held and positioned. Various mechanisms, such as clamps, fixtures, and automated positioning systems, are used to ensure stability during the cutting process.
Techniques Used in Micro Laser Cutting
Percussion Drilling
Percussion drilling is a technique that involves rapidly pulsing the laser beam to create holes or perforations in materials. This method is often used in micro drilling applications for creating tiny holes with high precision.
Ablation and Vaporization
Ablation and vaporization involve the controlled removal of material from the surface by the laser beam. These techniques are utilized in micro laser cutting to achieve precise cuts without physical contact, minimizing material damage.
Kerf Width Control
Kerf width refers to the width of material removed during the cutting process. Micro laser cutting techniques are designed to control and minimize kerf width, ensuring precision and preserving material integrity, especially in delicate applications.
Advantages of Micro Laser Cutting
Micro laser cutting presents several advantages that make it a preferred choice in various industries where precision and intricacy at a microscopic level are crucial. Some of the key advantages of micro laser cutting include:
1. Precision and Accuracy
Micro laser cutting technology offers unparalleled precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and cuts on a miniature scale. The focused laser beam enables the production of extremely fine features and tight tolerances, meeting the demands of industries requiring high precision components.
2. Minimal Material Damage
Compared to traditional cutting methods, micro laser cutting minimizes material damage during the cutting process. The focused nature of the laser beam reduces heat-affected zones, minimizing distortion, and preserving the material’s integrity, especially for delicate or heat-sensitive materials.
3. Versatility in Material Compatibility
Micro laser cutting is compatible with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, and semiconductors. This versatility makes it a valuable tool across diverse industries, from electronics and medical device manufacturing to aerospace and automotive applications.
4. Complex Geometries and Intricate Designs
The precision of micro laser cutting technology allows for the fabrication of complex geometries and intricate designs that are challenging or impossible to achieve using conventional cutting methods. This capability is particularly valuable in industries requiring miniaturized components with detailed features.
5. High-Speed Cutting
Micro laser cutting machines can operate at high speeds, significantly reducing production time while maintaining precision. This rapid cutting capability enhances productivity and efficiency in manufacturing processes, contributing to faster turnaround times for complex components.
6. Minimal Tooling Requirements
Unlike traditional cutting methods that may require complex tooling setups, micro laser cutting typically involves minimal tooling requirements. This reduces setup times and allows for quicker adaptation to design changes, making it a more flexible manufacturing solution.
7. Non-Contact Process
Micro laser cutting is a non-contact process, meaning there is no physical contact between the cutting tool and the workpiece. This absence of direct contact reduces the risk of contamination and wear on the cutting tool, resulting in longer tool life and consistent quality.
8. Scalability
Micro laser cutting technology is scalable, allowing for the production of both small-scale and large-scale batches of components with consistent precision and quality. This scalability makes it suitable for both prototyping and mass production needs.
9. Environmentally Friendly
Compared to some traditional cutting methods that involve chemicals or generate substantial waste, micro laser cutting is a relatively environmentally friendly process. It produces minimal waste, operates without the use of harmful chemicals, and can be energy-efficient when optimized.
The advantages of micro laser cutting, including its precision, minimal material damage, versatility, and ability to create intricate designs, have made it an indispensable technology across numerous industries. As technology continues to advance, further refinements in micro laser cutting techniques are anticipated, further enhancing its capabilities and expanding its applications in modern manufacturing processes.
Materials Used in Micro Laser Cutting
Micro laser cutting is a versatile technology capable of cutting various materials, both metals and non-metals, on a microscopic scale. The selection of materials depends on the application requirements, precision needed, and the specific characteristics of each material. Some of the materials commonly used in micro laser cutting include:
Metals
1. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a widely used metal in micro laser cutting stainless steel parts due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for intricate designs. It finds applications in industries such as electronics, medical devices, and automotive manufacturing.
2. Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal commonly used in micro laser cutting for its malleability and conductivity. It’s employed in various industries for manufacturing components like heat sinks, brackets, and aerospace parts.
3. Titanium
Titanium is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, making it an ideal material for medical implants and aerospace components that require both strength and lightweight properties.
4. Copper
Copper, valued for its excellent electrical conductivity, is used in micro laser cutting for creating intricate and fabrication electrical components, printed circuit boards (PCBs), and microelectronics.
Non-Metallic Materials
5. Plastics and Polymers
Various plastics and polymers, including acrylics, polycarbonates, polyimides, and PVC, are used in micro laser cutting due to their versatility, low cost, and ease of manipulation. They find applications in electronics, signage, and laser cut medical devices.
6. Ceramics
Ceramics like alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide are employed in micro laser cutting for their hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. They are used in industries such as aerospace, electronics, and medical technology for manufacturing sensors, insulators, and precision components.
7. Glass
Certain types of glass, such as borosilicate glass or quartz, are suitable for micro laser cutting due to their transparency, hardness, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Glass cutting is utilized in electronics, optics, and medical industries.
Semiconductor Materials
8. Silicon
Silicon is a fundamental material in semiconductor manufacturing. Micro laser cutting is used to process silicon wafers for creating microchips, sensors, and other electronic components.
Composite Materials
9. Carbon Fiber Composites
Carbon fiber composites are lightweight and possess high strength, making them suitable for aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment manufacturing. Micro laser cutting is used to shape these composites for intricate designs and components.
Micro laser cutting technology’s versatility in cutting various materials, including metals, non-metals, ceramics, and composites, is a key factor in its widespread adoption across industries. The ability to precisely cut and shape these materials at a microscopic level has revolutionized manufacturing processes, enabling the production of smaller, more intricate components that drive innovation in numerous sectors.
Applications of Micro Laser Cutting
Micro laser cutting, with its precision and ability to work on a microscopic scale, finds diverse applications across multiple industries. The technology’s capability to cut intricate shapes and create precise features on small components has made it indispensable in various sectors. Some prominent applications of micro laser cutting include:
Electronics Industry
- PCB Manufacturing: Micro laser cutting is used to create intricate circuitry and precise traces on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Its high precision enables the production of smaller, denser, and more complex PCBs used in smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices.
- Microelectronics Production: It plays a crucial role in manufacturing microelectronic components such as microchips, sensors, and small-scale electronic devices. The technology’s precision is essential for creating tiny features in these components.
Medical Device Fabrication
- Stents and Implants: Micro laser cutting is utilized in the production of medical devices like stents, catheters, and implants. Its ability to create intricate and precise structures is vital for medical implants that need to be biocompatible and tailored to fit specific anatomical needs.
- Microfluidics: In the field of lab-on-a-chip technology, micro laser cutting assists in creating intricate channels and structures on microfluidic devices used for medical diagnostics, drug delivery systems, and biochemical analysis.
Aerospace and Automotive Industries
- Fuel Injection Systems: Micro laser cutting is employed in manufacturing fuel injection nozzles and components in engines, ensuring precise flow control and efficiency in fuel delivery systems.
- Sensors and Actuators: It plays a role in producing miniature sensors and actuators used in aerospace and automotive applications, contributing to the functioning of various systems within aircraft and vehicles.
Micro-Optics and Photonics
- Optical Components: Micro laser cutting is used to fabricate micro-optical components such as lenses, mirrors, and waveguides for telecommunications, data transmission, and optical devices.
- Photonic Devices: It aids in the production of photonic devices used in lasers, sensors, and other optoelectronic applications, where precise shaping and cutting of optical materials are crucial.
Precision Engineering and Micro-Manufacturing
- Micro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS): Micro laser cutting is integral in manufacturing MEMS devices, which include microsensors, microvalves, and microactuators used in various industries, including robotics, healthcare, and consumer electronics.
- Precision Cutting for Miniature Parts: It is used to create tiny, precise components in miniature machinery, watches, and small mechanical parts, where conventional machining methods cannot achieve the required precision.
Micro laser cutting technology’s applications span across industries, enabling the fabrication of intricate and precise components critical for modern technologies. Its ability to work at a microscopic level continues to drive innovation in manufacturing, facilitating the production of smaller, more efficient, and technologically advanced products across various sectors.
China Top Micro Laser Cutting And Medical Laser Cutting Company
We are a full-service and best micro laser cutting and medical laser cut shop in China,Our company’s ultra-fine laser cutting machine can cut metal foil with a diameter of 0.01mm and punch micro holes with a diameter of 0.01mm. The oscillator is a sealed disk-type CO2 laser with an output power of 250W. This cutting machine can be used for trial production and mass production of thin IT products and electronic components or sheets that are difficult to process during precise assembly processes. The raw materials suitable for processing are thin sheet metals such as stainless steel or phosphor bronze with a thickness of 0.05~0.5mm.. With ultra-fine micro laser cutting service, we can help you take your project to the next level. We are very flexible and work with architects, students, custom medical device, jewelry designers, crafty people, entrepreneurs, moms, amateur rocketry enthusiasts, batmen, and Ryan Gosling impersonators, turning most jobs around in about a day.
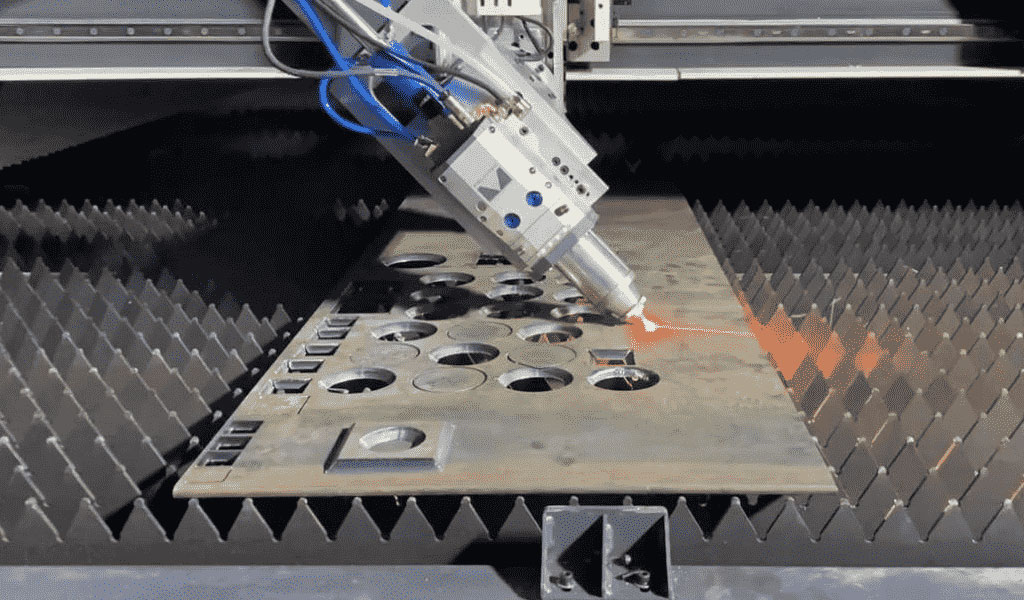
China Sheet Metal Fabrication Manufacturer
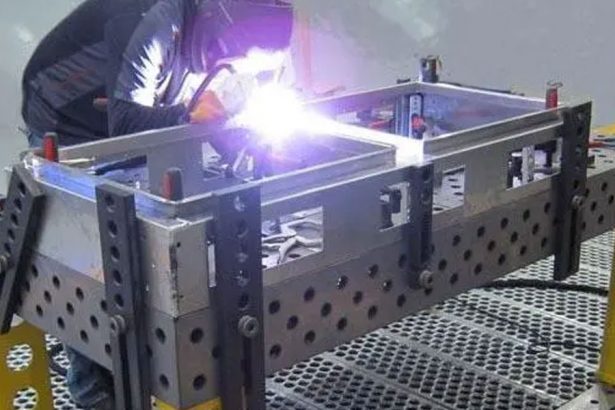
Custom precision metal fabrication services. Product specialties include UL® certified NEMA enclosures for various environmental conditions. Capabilities include punching, shearing, laser cutting, bending, machining, press brake forming, and welding. Materials worked with include mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Production volumes range from prototype to 10,000 pieces annually. Contract options include discrete orders, blanket orders, quarterly buys, and annual contracts. Value added services include inventory management, rapid prototyping, process development, design for manufacturability, inspection, supply chain management, transportation, and logistics. Industries served include aerospace, automotive, defense, electronic, electrical, entertainment, food and beverage, health, industrial automation, machinery, medical, oil, energy, power, sporting goods, telecommunications, transportation, and more.
using high quality materials
for your sheet metal parts orders
We uses a wide range of material selections for our sheet metal fabrication process. Among our materials are aluminum, stainless steel, brass, magnesium, copper, carbon steel, bronze, galvanized steel, and more. Each material is available in different grades and varieties. Rest assured that all the materials used for your sheet metal parts are durable, corrosion-resistant, long-lasting, rust-proof, wear-resistant, and high-performance. If you want a specific material to be used in the sheet metal fabrication process, don’t hesitate to contact us!
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Magnesium
- Bronze
- Galvanized Steel
Why BE-CU is Trusted by 1000+ Clients
Our sheet metal fabrication covers a lot of benefits to many industries, businesses, or projects. Below are the advantages of our services.
- Affordable and Fast Production:We can quickly produce different sheet metal prototypes and final products. KDM offers speedy production while assuring high precision. Our high-volume production also allows us to have cost-effect sheet metal fabrication services.
- Excellent Strength to Weight Ratio:Through our advanced sheet metal fabrication, we can produce sheet metal parts that are lightweight yet durable. We assure high strength, scratch resistance, and corrosion resistance to all produced sheet metal products.
- Wide Range of Materials and Techniques Used:We are experts in different sheet metal fabrication techniques that allow us to produce complex parts with additional intricate features such as notches, slots, holes, etc. Our wide range of sheet metal materials can also withstand electrical, high heat, corrosion, and more.
Online Contact China Precision Sheet Metal Manufacturers
As a direct supplier of precision machined and finished complete components to all segments of the aerospace, semiconductor, automotive, and medical industries, including innovative high tech startups, BE-CU Sheet metal manufacturer is your trusted source for precision sheet metal fabrication services.
To learn more about our aluminum,stainless steel and other steel alloy sheet metal fabrication services, contact us, or give us a call at +86 153 8731 8440, and one of our expert associates will assist you. BE-CU is your trusted source for premium sheet metal fabrication services and metal spinning china manufacturer.




