Steel is one of the most versatile and widely used materials in the modern world. Its exceptional strength, durability, and diverse range of properties have made it indispensable across various industries, from construction and automotive manufacturing to aerospace and infrastructure development. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of steel, exploring its different types, specifications, properties, and its numerous applications.
1.Understanding Steel
Steel is an alloy composed primarily of iron and varying amounts of carbon, which imparts its remarkable properties. In addition to iron and carbon, other elements such as manganese, silicon, and traces of other elements are often alloyed with steel to enhance its properties. These additives and the manufacturing process determine the characteristics of different types of steel.
2.Types of Steel
There are numerous types of steel, each tailored for specific applications based on their unique properties. Here are some of the most common ones:
- a. Carbon Steel: Carbon steel is the most basic type, containing minimal alloying elements. It is known for its exceptional strength and is used in various structural applications, including buildings and bridges.
- b. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel contains chromium, which provides excellent corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in the production of kitchen appliances, cutlery, medical instruments, and more.
- c. Alloy Steel: Alloy steel contains specific alloying elements like manganese, nickel, and molybdenum, giving it enhanced mechanical properties. It is used in applications like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
- d. Tool Steel: Tool steel is known for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It is utilized for making cutting tools, drills, and dies.
- e. High-Speed Steel: High-speed steel is a subset of tool steel that can withstand high temperatures without losing its hardness. It is often used for machining tools and drill bits.
3. Steel Specifications
Steel specifications are essential for ensuring the right material is used for a particular application. These specifications include:
- a. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) specifications, which define standards for various steel grades.
- b. AISI (American Iron and Steel Institute) codes for categorizing and classifying steel.
- c. EN (European Norm) standards for steel used in Europe.
- d. JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) for steel used in Japan.
- e. ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards for globally accepted steel specifications.
4. Properties of Steel
Steel boasts a wide range of properties that make it highly desirable in various applications:
- a. Strength: Steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, allowing it to support heavy loads and resist deformation.
- b. Durability: Steel is incredibly durable, with a long lifespan even in harsh conditions.
- c. Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel, in particular, offers excellent resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor or corrosive environments.
- d. Malleability: Steel can be easily molded and shaped into various forms, making it adaptable to diverse manufacturing processes.
- e. Conductivity: Some types of steel have excellent electrical conductivity, making them suitable for electrical applications.
5. Applications of Steel
The versatility of steel finds applications in almost every industry:
- a. Construction: Steel is widely used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure due to its strength and durability.
- b. Automotive: Steel’s high strength-to-weight ratio is crucial in the automotive industry, reducing fuel consumption and enhancing safety.
- c. Aerospace: Steel alloys play a significant role in the aerospace industry, where they are used in aircraft construction and engine components.
- d. Medical: Stainless steel is a preferred material for surgical instruments due to its corrosion resistance and biocompatibility.
- e. Energy: Steel is used in the production of wind turbines, nuclear power plants, and pipelines for the energy sector.
Conclusion
Steel, with its rich diversity of types, specifications, and properties, is a cornerstone of modern civilization. Its role in shaping industries, infrastructure, and everyday life cannot be overstated. Understanding the intricacies of steel is essential for making informed choices in various applications, ensuring the continued evolution of technology and society as a whole.
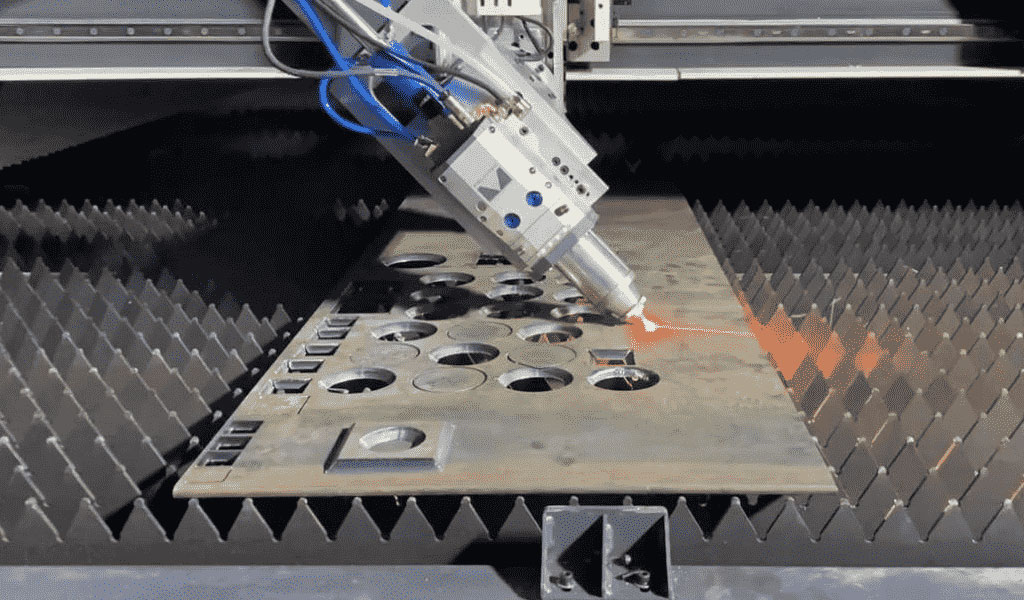
China Sheet Metal Fabrication Manufacturer
Custom precision metal fabrication services. Product specialties include UL® certified NEMA enclosures for various environmental conditions. Capabilities include punching, shearing, laser cutting, bending, machining, press brake forming, and welding. Materials worked with include mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Production volumes range from prototype to 10,000 pieces annually. Contract options include discrete orders, blanket orders, quarterly buys, and annual contracts. Value added services include inventory management, rapid prototyping, process development, design for manufacturability, inspection, supply chain management, transportation, and logistics. Industries served include aerospace, automotive, defense, electronic, electrical, entertainment, food and beverage, health, industrial automation, machinery, medical, oil, energy, power, sporting goods, telecommunications, transportation, and more.
using high quality materials
for your sheet metal parts orders
We uses a wide range of material selections for our sheet metal fabrication process. Among our materials are aluminum, stainless steel, brass, magnesium, copper, carbon steel, bronze, galvanized steel, and more. Each material is available in different grades and varieties. Rest assured that all the materials used for your sheet metal parts are durable, corrosion-resistant, long-lasting, rust-proof, wear-resistant, and high-performance. If you want a specific material to be used in the sheet metal fabrication process, don’t hesitate to contact us!
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Magnesium
- Bronze
- Galvanized Steel
Why BE-CU is Trusted by 1000+ Clients
Our sheet metal fabrication covers a lot of benefits to many industries, businesses, or projects. Below are the advantages of our services.
- Affordable and Fast Production:We can quickly produce different sheet metal prototypes and final products. KDM offers speedy production while assuring high precision. Our high-volume production also allows us to have cost-effect sheet metal fabrication services.
- Excellent Strength to Weight Ratio:Through our advanced sheet metal fabrication, we can produce sheet metal parts that are lightweight yet durable. We assure high strength, scratch resistance, and corrosion resistance to all produced sheet metal products.
- Wide Range of Materials and Techniques Used:We are experts in different sheet metal fabrication techniques that allow us to produce complex parts with additional intricate features such as notches, slots, holes, etc. Our wide range of sheet metal materials can also withstand electrical, high heat, corrosion, and more.
Online Contact China Precision Sheet Metal Manufacturers
As a direct supplier of precision machined and finished complete components to all segments of the aerospace, semiconductor, automotive, and medical industries, including innovative high tech startups, BE-CU Sheet metal manufacturer is your trusted source for precision sheet metal fabrication services.
To learn more about our aluminum,stainless steel and other steel alloy sheet metal fabrication services, contact us, or give us a call at +86 153 8731 8440, and one of our expert associates will assist you. BE-CU is your trusted source for premium sheet metal fabrication services and metal spinning china manufacturer.




