Metals have played a pivotal role in human civilization for centuries. From ancient tools and weapons to cutting-edge technology and infrastructure, metals have continuously evolved to meet the ever-changing needs of our society. This article delves into the fascinating world of metals, exploring various types of metals and their diverse and crucial applications across various industries.
Ferrous Metals
Ferrous metals are primarily composed of iron and include steel and cast iron. Their high strength, durability, and magnetic properties make them indispensable in many applications:
a. Steel:
- Construction: Used in beams, columns, and reinforcement bars for building stability.
- Transportation: Forms the framework of vehicles, ships, and aircraft.
- Kitchenware: Stainless steel is prevalent for utensils and appliances.
b. Cast Iron:
- Pipes and Fittings: Water distribution and sewage systems.
- Cookware: Known for its heat retention, it’s ideal for griddles and pans.
- Engine Blocks: Used in automotive and machinery manufacturing.
Non-Ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals do not contain significant amounts of iron and encompass a wide range of materials, each with unique characteristics:
a. Aluminum:
- Aerospace: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, used in aircraft manufacturing.
- Packaging: Beverage cans, foils, and containers.
- Construction: Facades, windows, and roofing materials.
b. Copper:
- Electrical Wiring: Excellent conductor of electricity.
- Plumbing: Durable, corrosion-resistant pipes and fittings.
- Art and Sculpture: Prized for its malleability and color.
c. Gold:
- Jewelry: Valued for its beauty and rarity.
- Electronics: Used in circuit boards and connectors.
- Dentistry: Gold alloys are employed in dental crowns.
d. Silver:
- Photography: Silver compounds in photographic film.
- Jewelry and Ornaments: Popular for its lustrous appearance.
- Medicine: Silver nanoparticles in wound dressings for their antibacterial properties.
Alloys
Metals are often combined to create alloys, which inherit the best properties of their constituent elements:
a. Bronze:
- Sculptures and Statues: Known for its artistic value.
- Bearings: Low friction and high durability.
b. Brass:
- Musical Instruments: Trumpets, saxophones, and more.
- Decorative Hardware: Handles, doorknobs, and faucets.
c. Stainless Steel:
- Medical Instruments: Hygienic and corrosion-resistant.
- Kitchen Appliances: Resists staining and rust.
Precious Metals
Precious metals are valued for their rarity and aesthetic appeal:
a. Platinum:
- Jewelry: Resistant to tarnish, ideal for engagement rings.
- Catalytic Converters: Used in reducing emissions from automobiles.
b. Palladium:
- Automotive Catalysts: Effective in reducing emissions.
- Jewelry: A more affordable alternative to platinum.
Conclusion
Metals are the backbone of modern society, serving as the building blocks for countless products and innovations. Whether ferrous or non-ferrous, alloys or precious metals, each type has its unique properties that make it indispensable across various industries. As technology advances and environmental concerns grow, the role of metals in shaping our world will continue to evolve, creating a sustainable and vibrant future built on the foundations of these remarkable materials.
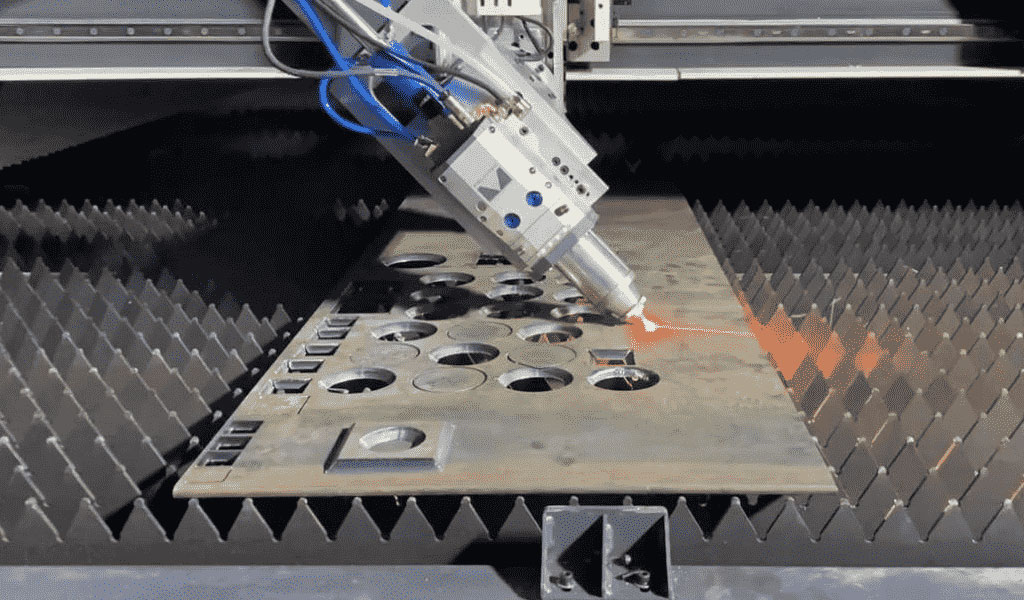
China Sheet Metal Fabrication Manufacturer
Custom precision metal fabrication services. Product specialties include UL® certified NEMA enclosures for various environmental conditions. Capabilities include punching, shearing, laser cutting, bending, machining, press brake forming, and welding. Materials worked with include mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Production volumes range from prototype to 10,000 pieces annually. Contract options include discrete orders, blanket orders, quarterly buys, and annual contracts. Value added services include inventory management, rapid prototyping, process development, design for manufacturability, inspection, supply chain management, transportation, and logistics. Industries served include aerospace, automotive, defense, electronic, electrical, entertainment, food and beverage, health, industrial automation, machinery, medical, oil, energy, power, sporting goods, telecommunications, transportation, and more.
using high quality materials
for your sheet metal parts orders
We uses a wide range of material selections for our sheet metal fabrication process. Among our materials are aluminum, stainless steel, brass, magnesium, copper, carbon steel, bronze, galvanized steel, and more. Each material is available in different grades and varieties. Rest assured that all the materials used for your sheet metal parts are durable, corrosion-resistant, long-lasting, rust-proof, wear-resistant, and high-performance. If you want a specific material to be used in the sheet metal fabrication process, don’t hesitate to contact us!
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Magnesium
- Bronze
- Galvanized Steel
Why BE-CU is Trusted by 1000+ Clients
Our sheet metal fabrication covers a lot of benefits to many industries, businesses, or projects. Below are the advantages of our services.
- Affordable and Fast Production:We can quickly produce different sheet metal prototypes and final products. KDM offers speedy production while assuring high precision. Our high-volume production also allows us to have cost-effect sheet metal fabrication services.
- Excellent Strength to Weight Ratio:Through our advanced sheet metal fabrication, we can produce sheet metal parts that are lightweight yet durable. We assure high strength, scratch resistance, and corrosion resistance to all produced sheet metal products.
- Wide Range of Materials and Techniques Used:We are experts in different sheet metal fabrication techniques that allow us to produce complex parts with additional intricate features such as notches, slots, holes, etc. Our wide range of sheet metal materials can also withstand electrical, high heat, corrosion, and more.
Online Contact China Precision Sheet Metal Manufacturers
As a direct supplier of precision machined and finished complete components to all segments of the aerospace, semiconductor, automotive, and medical industries, including innovative high tech startups, BE-CU Sheet metal manufacturer is your trusted source for precision sheet metal fabrication services.
To learn more about our aluminum,stainless steel and other steel alloy sheet metal fabrication services, contact us, or give us a call at +86 153 8731 8440, and one of our expert associates will assist you. BE-CU is your trusted source for premium sheet metal fabrication services and metal spinning china manufacturer.




