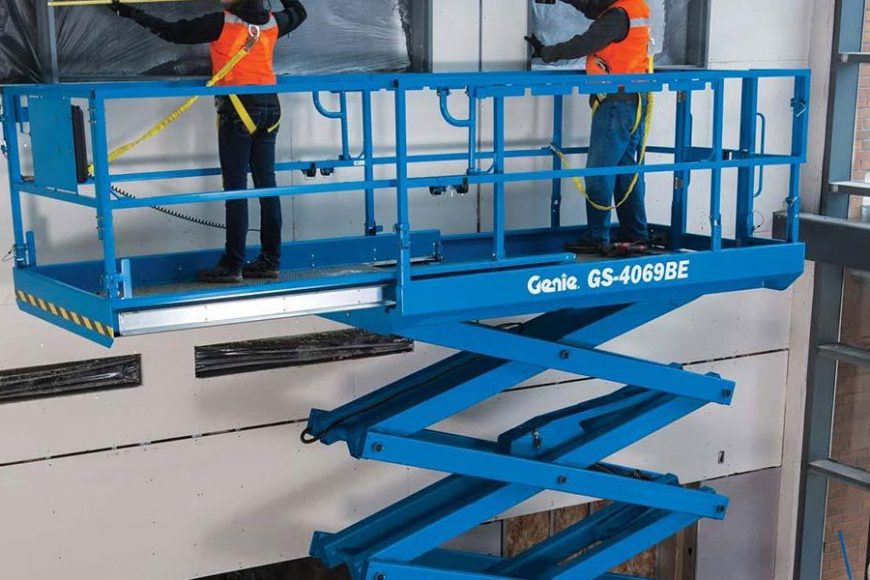
In the realm of construction, maintenance, and various industrial operations, aerial work platforms (AWPs) serve as indispensable tools. These versatile machines provide access to heights and locations that would otherwise be challenging or unsafe to reach. An AWP’s functionality relies on a sophisticated interplay of several key components, each contributing to its overall performance and safety. This article aims to explore and dissect the three fundamental components that form the backbone of aerial work platforms, shedding light on their importance and functionality.
Introduction to Aerial Work Platforms
Before delving into the core components of AWPs, it’s essential to understand their significance and applications. Aerial work platforms, commonly referred to as aerial lifts or elevated work platforms, encompass a wide array of machinery designed to elevate workers, tools, and materials to different heights. These platforms find extensive use in construction, maintenance tasks, firefighting, rescue operations, and various industrial applications.
AWPs come in diverse types, including scissor lifts, boom lifts, vertical mast lifts, and personnel lifts, among others. Each type caters to specific operational needs, providing distinct capabilities in terms of reach, height, mobility, and load-bearing capacity.
The Three Basic Components of Aerial Work Platforms
1. Platform Structure
The platform structure serves as the foundation of an aerial work platform, constituting the area where workers, equipment, and materials are placed during operations. This component is crafted to withstand dynamic loads while ensuring stability and safety for the occupants.
a. Base and Chassis
The base and chassis form the structural framework that supports the entire AWP. Constructed from sturdy materials such as steel or aluminum, these components provide stability and structural integrity. The base incorporates features like outriggers or stabilizers to enhance balance, especially when the platform is elevated.
b. Platform Deck
The platform deck is the elevated surface where operators stand or position equipment. It’s typically equipped with guardrails, toe boards, and gates to prevent falls and ensure worker safety. Materials used for the platform deck are chosen for their durability and non-slip properties to offer a secure working environment.
c. Controls and Operator Compartment
Controls play a pivotal role in maneuvering the AWP. These include joysticks, buttons, or levers situated within the operator compartment, enabling precise movement and operation of the platform. The operator compartment is designed ergonomically to ensure comfort and ease of use for the personnel handling the machine.
2. Lifting Mechanism
The lifting mechanism forms the core operational aspect of an AWP, enabling vertical or horizontal movement of the platform. It facilitates the extension and retraction of the platform to reach varying heights and positions.
a. Hydraulic System
Most AWPs utilize hydraulic systems to power their lifting mechanisms. Hydraulic cylinders, pumps, and valves work in unison to control the extension and retraction of the platform. This system provides the necessary force to lift the platform while ensuring smooth and controlled movements.
b. Telescopic or Articulating Boom
Depending on the type of AWP, the lifting mechanism might consist of a telescopic boom or an articulating arm. Telescopic booms extend vertically or horizontally using hydraulic cylinders, allowing access to different heights and distances. Articulating arms comprise multiple sections that articulate or bend, providing enhanced maneuverability to reach challenging spots.
3. Propulsion and Mobility System
The mobility system enables the AWP to navigate across diverse terrains and maneuver into position efficiently. It comprises various components that power and control the machine’s movement.
a. Power Source
AWPs commonly rely on electric, diesel, gasoline, or hybrid power sources. Electric-powered AWPs are favored for indoor applications due to their quieter operation and zero emissions. On the other hand, diesel or gasoline-powered units offer greater mobility and are suitable for outdoor use.
b. Drive and Steering Mechanism
The drive and steering mechanism allows the AWP to move forwards, backwards, or steer in different directions. Depending on the model, AWPs feature various drive systems such as wheels, tracks, or a combination of both. These systems enable precise maneuvering, essential for positioning the platform accurately.
c. Safety Features and Controls
Integrated safety features are critical in ensuring the secure operation of an AWP. These include emergency stop buttons, overload sensors, tilt alarms, and interlocks to prevent unauthorized use. Additionally, control systems manage the speed, direction, and operation of the AWP, enhancing overall safety and efficiency.
Conclusion
Aerial work platforms have revolutionized the way tasks at height are performed, providing safe and efficient access to elevated areas. Understanding the intricate components that constitute these machines is crucial for proper operation, maintenance, and ensuring the safety of personnel using them. The platform structure, lifting mechanism, and propulsion and mobility system collectively define the functionality and capabilities of an AWP, making them indispensable tools across various industries.
As technology continues to evolve, advancements in materials, design, and safety features will further enhance the efficiency and safety standards of aerial work platforms. Continual innovation in these fundamental components will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of AWPs, making them more versatile, reliable, and safer for operators in diverse working environments.
China Sheet Metal Fabrication Manufacturer
Custom precision metal fabrication services. Product specialties include UL® certified NEMA enclosures for various environmental conditions. Capabilities include punching, shearing, laser cutting, bending, machining, press brake forming, and welding. Materials worked with include mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Production volumes range from prototype to 10,000 pieces annually. Contract options include discrete orders, blanket orders, quarterly buys, and annual contracts. Value added services include inventory management, rapid prototyping, process development, design for manufacturability, inspection, supply chain management, transportation, and logistics. Industries served include aerospace, automotive, defense, electronic, electrical, entertainment, food and beverage, health, industrial automation, machinery, medical, oil, energy, power, sporting goods, telecommunications, transportation, and more.
using high quality materials
for your sheet metal parts orders
We uses a wide range of material selections for our sheet metal fabrication process. Among our materials are aluminum, stainless steel, brass, magnesium, copper, carbon steel, bronze, galvanized steel, and more. Each material is available in different grades and varieties. Rest assured that all the materials used for your sheet metal parts are durable, corrosion-resistant, long-lasting, rust-proof, wear-resistant, and high-performance. If you want a specific material to be used in the sheet metal fabrication process, don’t hesitate to contact us!
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Magnesium
- Bronze
- Galvanized Steel
Why BE-CU is Trusted by 1000+ Clients
Our sheet metal fabrication covers a lot of benefits to many industries, businesses, or projects. Below are the advantages of our services.
- Affordable and Fast Production:We can quickly produce different sheet metal prototypes and final products. KDM offers speedy production while assuring high precision. Our high-volume production also allows us to have cost-effect sheet metal fabrication services.
- Excellent Strength to Weight Ratio:Through our advanced sheet metal fabrication, we can produce sheet metal parts that are lightweight yet durable. We assure high strength, scratch resistance, and corrosion resistance to all produced sheet metal products.
- Wide Range of Materials and Techniques Used:We are experts in different sheet metal fabrication techniques that allow us to produce complex parts with additional intricate features such as notches, slots, holes, etc. Our wide range of sheet metal materials can also withstand electrical, high heat, corrosion, and more.
Online Contact China Precision Sheet Metal Manufacturers
As a direct supplier of precision machined and finished complete components to all segments of the aerospace, semiconductor, automotive, and medical industries, including innovative high tech startups, BE-CU Sheet metal manufacturer is your trusted source for precision sheet metal fabrication services.
To learn more about our aluminum,stainless steel and other steel alloy sheet metal fabrication services, contact us, or give us a call at +86 153 8731 8440, and one of our expert associates will assist you. BE-CU is your trusted source for premium sheet metal fabrication services and metal spinning china manufacturer.




