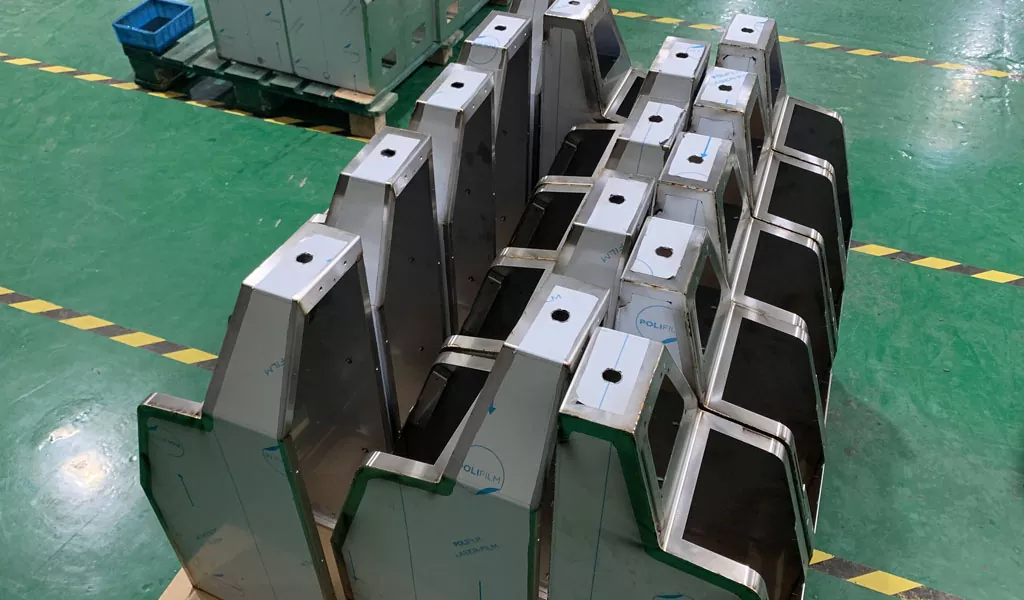
The importance of enclosures in electronic products cannot be overemphasized. Designing a sheet metal enclosure involves several considerations to ensure functionality, aesthetics, manufacturability, and overall performance. Enclosures have become increasingly popular due to their benefits, such as electrical conductivity, emission reduction, and resistance to harsh industrial environments.
Sheet metal fabrication aims to ensure the overall design successfully meets market and client demands while providing a positive user experience.Creating high-quality enclosures can help achieve this when it comes to electronic components. There are some sets of guidelines associated with sheet metal enclosure design. A good understanding of these guidelines will make the job easier and help ensure quality outcomes.
The following sheet metal enclosure design tips explain the details of the enclosure design to keep your work up to standard. Let’s dive right into it!
Clear the Sheet Metal Enclosure Design Requirements
Certainly! Here are some common requirements to consider when designing a sheet metal enclosure:
Size and Shape:
Determine the overall dimensions of the enclosure based on the space requirements and the components it needs to house.
Consider any specific shape requirements or constraints based on the application or available space.
Material Selection:
Choose a suitable sheet metal material based on factors such as strength, durability, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and cost.
Common options include stainless steel, aluminum, galvanized steel, and mild steel.
Structural Integrity:
Design the enclosure to provide sufficient strength and rigidity to protect the internal components.
Consider factors such as load-bearing capacity, reinforcement structures, and support for mounting accessories.
Accessibility and Openings:
Determine the location and size of openings, slots, holes, and cutouts for access to internal components, connectors, switches, and interfaces.
Ensure proper alignment and spacing for connectors and cable management.
Cooling and Ventilation:
Incorporate features such as vents, fan mounts, or heat sinks to facilitate cooling and airflow within the enclosure, if required.
Consider the thermal management needs of sensitive components.
EMI/RFI Shielding:
If electromagnetic or radio frequency interference shielding is required, plan for shielding measures such as conductive gaskets, grounding points, or additional layers of shielding material.
Environmental Protection:
Consider the environmental conditions the enclosure will be exposed to, such as moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures.
Design seals, gaskets, or ingress protection (IP) ratings to ensure adequate protection against environmental elements.
Mounting and Assembly:
Determine the mounting options required for the enclosure, such as wall mounting, panel mounting, or rack mounting.
Ensure ease of assembly and disassembly by incorporating appropriate fastening methods and alignment features.
Finishing and Aesthetics:
Decide on the desired surface finish, whether it’s paint, powder coating, anodizing, or other protective and visually appealing treatments.
Consider any branding, labeling, or identification requirements.
Compliance and Certifications:
If the enclosure needs to meet specific industry standards or certifications, design the enclosure to comply with the required specifications and guidelines.
These requirements will vary depending on the specific application and industry. It is important to consider all relevant factors and consult with experts in sheet metal fabrication to ensure a successful enclosure design.
A good product is the result of ingenious design and scientific solutions.
Be-Cu
Find the Suitable Materials for Your Sheet Metal Enclosure
When selecting materials for a sheet metal enclosure, several factors need to be considered, such as strength, corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, weight, cost, and specific application requirements. Here are some commonly used materials for sheet metal enclosures:
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability.
It offers good strength and can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
Common stainless steel grades for enclosures include 304, 316, and 430.
Aluminum:
Aluminum is lightweight, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
It has good corrosion resistance, especially when treated or anodized.
Aluminum is electrically conductive and can help with heat dissipation.
Common aluminum alloys for enclosures include 5052, 6061, and 6063.
Galvanized Steel:
Galvanized steel is carbon steel coated with a layer of zinc to enhance corrosion resistance.
It offers good strength and is cost-effective compared to stainless steel or aluminum.
Galvanized steel is commonly used for outdoor enclosures or applications prone to moisture.
Mild Steel:
Mild steel, also known as carbon steel, is strong and relatively low-cost.
It is widely available and easy to work with in terms of fabrication and welding.
However, mild steel is susceptible to corrosion, so proper coating or painting is necessary for protection.
Copper:
Copper is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, making it suitable for certain applications.
It has good corrosion resistance and is often used for electrical enclosures or applications requiring high conductivity.
Copper can be expensive compared to other materials, so its use depends on specific requirements.
Other Materials:
Depending on the application, other materials like brass or specific alloys may be suitable for specialized enclosures.
Non-metallic materials like fiberglass or plastic composites might be considered for applications requiring insulation, lightweight construction, or chemical resistance.
Find the Suitable Applications for Your Sheet Metal Enclosure
Sheet metal enclosures are widely used in various industries for housing and protecting electronic components, equipment, and systems. Here are some suitable applications where sheet metal enclosures are commonly utilized:
Electronics and Telecommunications:
Enclosures for electronic devices such as computers, servers, routers, and telecommunication equipment.
Control panels and cabinets for industrial automation and process control systems.
Enclosures for power distribution equipment, circuit breakers, and electrical panels.
Industrial Machinery and Equipment:
Enclosures for machine control units, motor drives, and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems.
Cabinets for manufacturing equipment, including CNC machines, robotics, and automated systems.
Instrumentation enclosures for measuring devices, sensors, and data acquisition systems.
Medical and Healthcare:
Enclosures for medical equipment like diagnostic devices, imaging systems, and patient monitoring systems.
Cabinets for laboratory equipment, analytical instruments, and testing devices.
Enclosures for healthcare IT infrastructure, including servers, networking, and data storage systems.
Automotive and Transportation:
Enclosures for vehicle control units, electronic systems, and automotive diagnostic equipment.
Mounting cabinets for transportation infrastructure, such as toll collection systems or traffic control devices.
Enclosures for railway signaling equipment, ticketing systems, and communication devices.
Aerospace and Defense:
Enclosures for avionics systems, flight control units, and navigation equipment in aircraft.
Ruggedized enclosures for military electronics, communication systems, and radar equipment.
Cabinets for satellite communication systems, ground control stations, and missile guidance systems.
Energy and Utilities:
Enclosures for renewable energy systems like solar inverters, wind turbine control units, and battery management systems.
Cabinets for electrical substations, distribution panels, and power generation equipment.
Enclosures for utility meters, smart grid devices, and energy management systems.
These are just a few examples of the many applications where sheet metal enclosures are utilized. The versatility, durability, and customizable nature of sheet metal make it a suitable choice for a wide range of industries and equipment. The specific requirements of each application should be considered when designing and selecting a sheet metal enclosure.
Choose the Right Shape of Your Custom Sheet Metal Enclosure
The choice of the shape for a custom sheet metal enclosure depends on several factors, including functionality, space constraints, aesthetics, and manufacturing feasibility. Here are some common shapes to consider for sheet metal enclosures:
Rectangular or Cuboid:
Rectangular or cuboid-shaped enclosures are straightforward and easy to design and manufacture.
They provide efficient use of space and can accommodate various internal components.
This shape is commonly used when space is not a constraint, and a simple, box-like design is desired.
Cylindrical or Tubular:
Cylindrical or tubular enclosures are suitable for applications where a round shape is preferred or necessary.
They can provide structural integrity and are often used for housing cylindrical or tubular components.
Cylindrical enclosures can be designed with removable end caps or hinged access points for easy maintenance.
L-Shaped or T-Shaped:
L-shaped or T-shaped enclosures are useful when multiple components or compartments need to be housed within a single enclosure.
This shape allows for efficient organization and separation of different functional areas or components.
It is commonly used in control panels or enclosures with distinct sections for different purposes.
Sloped or Angled:
Sloped or angled enclosures offer ergonomic design and improved visibility of displays or control interfaces.
They can enhance user interaction and provide a modern, sleek appearance.
This shape is often used in applications such as control consoles, display panels, or equipment with an operator interface.
Custom Contoured:
Depending on the specific requirements or aesthetics of the application, custom contoured shapes can be designed.
These shapes may incorporate curves, chamfers, or unique features to meet specific design or functional criteria.
Custom contoured enclosures can provide a distinctive appearance or fit into specific spaces or equipment configurations.
When choosing the shape, it is important to consider factors such as internal component layout, ease of assembly, access to components, structural integrity, and any specific design constraints. Consulting with sheet metal fabrication experts or design engineers can help ensure that the chosen shape aligns with the functional, aesthetic, and manufacturing requirements of the custom sheet metal enclosure.
Understand the Thickness of Sheet Metal Enclosure
The thickness of sheet metal for an enclosure is a crucial consideration that impacts its structural integrity, durability, and manufacturing process. Here are some key points to understand regarding sheet metal thickness for enclosures:
Gauge Measurement:
Sheet metal thickness is typically measured using gauge numbers, which represent different thicknesses.
The lower the gauge number, the thicker the sheet metal. For example, 14-gauge sheet metal is thicker than 18-gauge sheet metal.
Common gauge sizes for sheet metal enclosures range from 16-gauge (approximately 0.0598 inches or 1.52 mm) to 22-gauge (approximately 0.0299 inches or 0.76 mm).
Application and Strength Requirements:
The choice of sheet metal thickness depends on the specific application and the strength required for the enclosure.
Thicker sheet metal provides greater strength and rigidity, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications or when additional structural support is necessary.
Thinner sheet metal can be used for lighter-duty applications or when weight reduction is a factor.
Material and Forming Considerations:
Different materials have different inherent strengths and characteristics. For example, stainless steel is typically stronger than aluminum of the same thickness.
The material and its tensile strength should be taken into account when determining the appropriate thickness for the desired level of durability and performance.
Consider the forming or fabrication processes involved, as certain thicknesses may be more suitable for specific bending, welding, or forming techniques.
Design and Dimensional Stability:
Thicker sheet metal can better resist deformation and maintain dimensional stability, particularly for larger enclosures or when subjected to external forces or vibrations.
Thinner sheet metal may require additional reinforcement or stiffeners to maintain structural integrity.
Manufacturing Considerations:
Sheet metal thickness can affect the ease of fabrication and manufacturing processes.
Thicker sheet metal may require more powerful equipment or specialized machinery for cutting, bending, and welding.
Thinner sheet metal can be more flexible and easier to work with but may require careful handling to avoid distortion during fabrication.
It is important to balance the strength requirements, application considerations, manufacturing capabilities, and design constraints when selecting the appropriate sheet metal thickness for an enclosure. Consultation with sheet metal fabrication professionals or engineers can provide valuable guidance in determining the optimal thickness for your specific enclosure design and requirements.
Finishing Options For Sheet Metal Enclosure
When it comes to finishing options for sheet metal enclosures, there are several choices available to enhance the appearance, protect against corrosion, and meet specific application requirements. Here are some common finishing options:
Painting:
Painting is a popular and versatile finishing option for sheet metal enclosures.
It provides a wide range of colors and finishes to achieve desired aesthetics.
Paints can also provide additional protection against corrosion and environmental elements.
Pre-treatment processes, such as cleaning, priming, and powder coating, are often employed for optimal paint adhesion and durability.
Powder Coating:
Powder coating is a durable and environmentally friendly finishing method for sheet metal enclosures.
It involves applying a dry powder electrostatically and then curing it with heat to form a hard, protective coating.
Powder coating offers excellent resistance to scratches, chemicals, and UV rays.
It provides a wide range of color options, textures, and special effects.
Anodizing:
Anodizing is commonly used for aluminum enclosures to enhance corrosion resistance and provide an attractive finish.
The process involves creating an oxide layer on the surface of the aluminum by electrolytic treatment.
Anodizing can produce various colors, including clear or transparent coatings.
It provides increased hardness and wear resistance while maintaining the natural metallic appearance.
Plating:
Plating involves applying a thin layer of metal onto the sheet metal surface, typically using processes like electroplating or electroless plating.
Plating options include chrome, nickel, zinc, or other metals.
Plating can provide aesthetic appeal, corrosion resistance, and improved conductivity.
It is often used for decorative or functional purposes, such as achieving a reflective or conductive surface.
Brushed or Polished Finish:
Brushing or polishing the sheet metal surface can create a visually appealing and smooth finish.
Brushing creates a consistent pattern of fine lines on the metal surface, while polishing provides a reflective and glossy appearance.
These finishes are often used for high-end applications or when a clean, sophisticated look is desired.
Protective Coatings:
In addition to the aforementioned options, protective coatings like clear lacquers, epoxy coatings, or silicone-based coatings can be applied to provide additional resistance to moisture, chemicals, or abrasion.
Protective coatings can help preserve the appearance and durability of the sheet metal enclosure.
The choice of finishing option depends on the desired aesthetics, functional requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Consulting with a sheet metal fabrication professional can provide valuable insights and guidance in selecting the most suitable finishing option for your specific sheet metal enclosure.
China Sheet Metal Fabrication Manufacturer
Custom precision metal fabrication services. Product specialties include UL® certified NEMA enclosures for various environmental conditions. Capabilities include punching, shearing, laser cutting, bending, machining, press brake forming, and welding. Materials worked with include mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Production volumes range from prototype to 10,000 pieces annually. Contract options include discrete orders, blanket orders, quarterly buys, and annual contracts. Value added services include inventory management, rapid prototyping, process development, design for manufacturability, inspection, supply chain management, transportation, and logistics. Industries served include aerospace, automotive, defense, electronic, electrical, entertainment, food and beverage, health, industrial automation, machinery, medical, oil, energy, power, sporting goods, telecommunications, transportation, and more.
using high quality materials
for your sheet metal parts orders
We uses a wide range of material selections for our sheet metal fabrication process. Among our materials are aluminum, stainless steel, brass, magnesium, copper, carbon steel, bronze, galvanized steel, and more. Each material is available in different grades and varieties. Rest assured that all the materials used for your sheet metal parts are durable, corrosion-resistant, long-lasting, rust-proof, wear-resistant, and high-performance. If you want a specific material to be used in the sheet metal fabrication process, don’t hesitate to contact us!
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Brass
- Copper
- Magnesium
- Bronze
- Galvanized Steel
Why BE-CU is Trusted by 1000+ Clients
Our sheet metal fabrication covers a lot of benefits to many industries, businesses, or projects. Below are the advantages of our services.
- Affordable and Fast Production:We can quickly produce different sheet metal prototypes and final products. KDM offers speedy production while assuring high precision. Our high-volume production also allows us to have cost-effect sheet metal fabrication services.
- Excellent Strength to Weight Ratio:Through our advanced sheet metal fabrication, we can produce sheet metal parts that are lightweight yet durable. We assure high strength, scratch resistance, and corrosion resistance to all produced sheet metal products.
- Wide Range of Materials and Techniques Used:We are experts in different sheet metal fabrication techniques that allow us to produce complex parts with additional intricate features such as notches, slots, holes, etc. Our wide range of sheet metal materials can also withstand electrical, high heat, corrosion, and more.
Online Contact China Precision Sheet Metal Manufacturers
As a direct supplier of precision machined and finished complete components to all segments of the aerospace, semiconductor, automotive, and medical industries, including innovative high tech startups, BE-CU Sheet metal manufacturer is your trusted source for precision sheet metal fabrication services.
To learn more about our aluminum,stainless steel and other steel alloy sheet metal fabrication services, contact us, or give us a call at +86 153 8731 8440, and one of our expert associates will assist you. BE-CU is your trusted source for premium sheet metal fabrication services and metal spinning china manufacturer.




